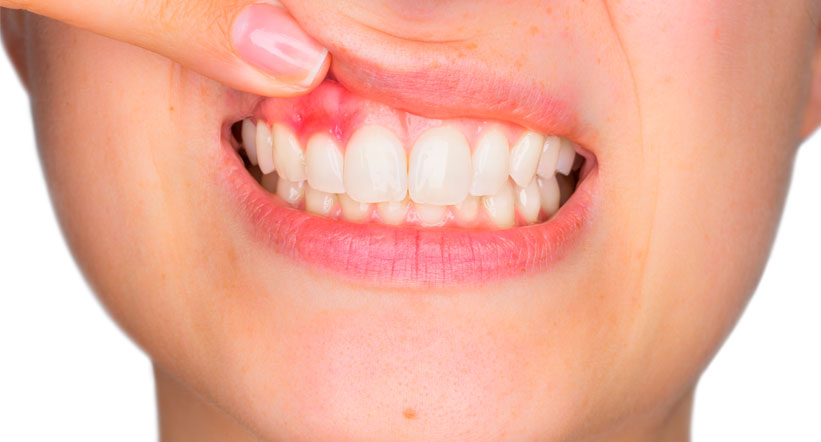
Periodontitis (also known as periodontal disease or pyorrhoea) is a bacterial infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth: the gums, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone.
The whole of these tissues is called periodontium and has the task of keeping the teeth together with the bone tissue, giving it support and stability. Hence the name: periodontitis is a disease that affects these tissues.
What are the most common causes of periodontitis?
The presence of plaque, genetic predisposition but also smoke or malocclusion: these are all factors that can lead to the onset of this inflammation.
When there is a lack of constant oral hygiene, the bacteria trigger an inflammatory process that causes irritation and bleeding of the gums, or an inflammation known as gingivitis. Periodontitis can develop when the gingivitis is not treated properly and becomes chronic.
Specifically, inflammation is caused by the accumulation of bacterial plaque above and below the gumline (the area where the gum meets the tooth).
What are the effects of periodontitis?
The groove between the tooth and the gum becomes deeper and "gum pockets" are formed, pockets where bacteria lurk and proliferate, causing inflammation that can lead to irreversible damage to the tissues that support the teeth such as erosion or destruction of the bone, ligament and recession of the gum.
Periodontitis is the final stage in the evolution of gum disease. Unlike gingivitis, it is a non-reversible condition that has serious consequences for the appearance and health of teeth and gums.
Without adequate treatment, advanced periodontitis causes instability of the teeth that may fall out or need to be removed by the dentist.
Periodontitis is therefore the most serious stage of gum disease: it is irreversible and can lead to permanent tooth loss and therefore requires medical or dental treatment.
How to prevent periodontitis?
It is very important not to ignore the first signs of this infection and recognize its first symptoms. Seeing blood as we brush our teeth or floss, having bad breath and reddened or swollen gums are all signs of gum disease. The most characteristic symptoms of periodontitis are:
- Bleeding gums
- Gingival recesses
- Halitosis
- Sensitivity to heat and cold
- Teeth moving or changing position
If you notice these symptoms, it is important to discuss them immediately with a professional dentist who can advise you on the best ways to treat them before the problem gets worse.
How to treat periodontitis?
To treat periodontitis it is necessary to remove the bacterial plaque accumulated in the periodontal pockets. The initial therapy consists of one or more sessions of professional dental cleaning, followed by treatments that allow the removal of plaque and tartar in the region under the gum.
At an advanced stage of the disease, surgical treatments are required to eliminate periodontal pockets and restore stability to the teeth.
The medical team at Degidi Clinic is made up of highly experienced, internationally recognised surgeons and dentists. We want to offer the best solutions to the problems that our patients present. This encourages us to constantly seek out the most effective and least invasive solutions, including innovative solutions.
After performing the surgical treatment, it is advisable to carry out periodic checks to prevent the disease from recurring and to pay close attention to daily oral hygiene.
This includes: brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a toothpaste specifically designed for gum disease; flossing or brushing your teeth every day; and regular check-ups with your dentist.
If periodontitis is not treated properly and teeth are lost, it is very important to act quickly and replace them immediately.
There are various techniques for replacing missing teeth, the most common being dental implantology.
Dental implantology is the pride of the Degidi dental clinic, a leading dental centre based in Bologna.
Contact us for more information on all our services, we will help you find the best solution for your needs.